Understanding the Voltage Ratings of High Voltage Capacitor Units for Reliable Power Systems
High Quality OEM High Voltage Capacitor Unit Wholesaler
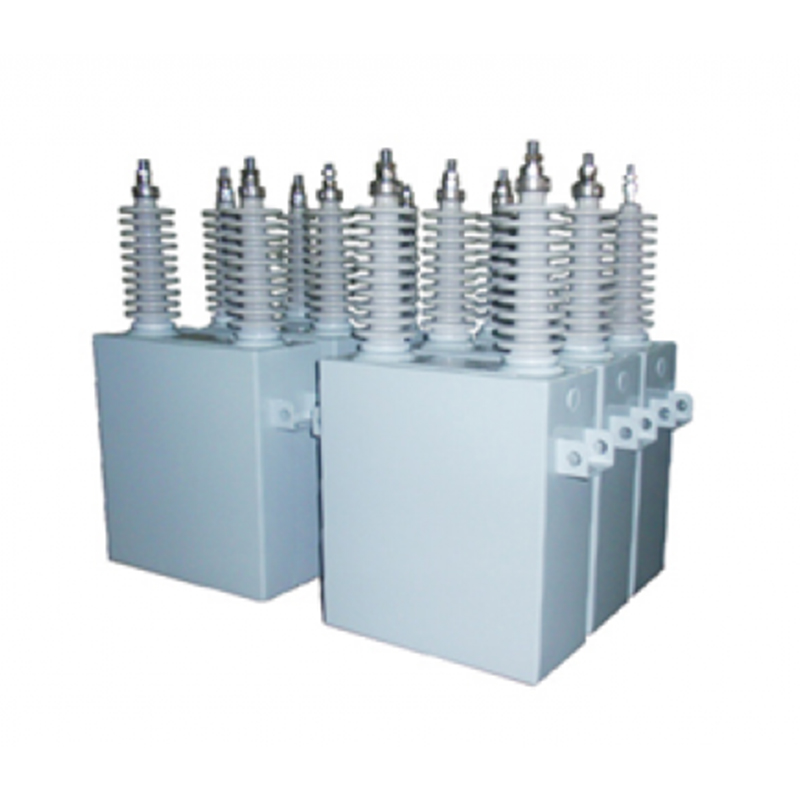
The High Voltage Capacitor Unit is a crucial component in electrical power systems, known for its ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. Given the importance of High Voltage Capacitor Units in maintaining the stability and efficiency of power networks, it is essential to comprehend the different voltage ratings of these units. The voltage rating of a High Voltage Capacitor Unit is a critical specification that indicates the voltage level it can withstand without breaking down.

In the context of High Voltage Capacitor Units, the term "voltage rating" refers to the AC voltage that the capacitor can handle continuously without exceeding specified limits of dielectric loss and temperature rise. It is expressed in terms of a peak or RMS value and is an important factor in determining the capacitor's suitability for a particular application.
The voltage ratings for High Voltage Capacitor Units can vary widely, and they are often categorized into different classes to suit various applications. For instance, some common voltage ratings for High Voltage Capacitor Units include 2kV, 4kV, 6kV, and even higher, 30kV or more for specific industrial applications. These ratings are not arbitrary; they are determined by the material properties of the dielectric used in the capacitor, the design of the capacitor's construction, and the specific requirements of the application in which the High Voltage Capacitor Unit will be used.
The selection of the appropriate voltage rating for a High Voltage Capacitor Unit is influenced by several factors. The voltage rating must be compatible with the voltage levels present in the electrical system where the High Voltage Capacitor Unit will be installed. Mismatching the voltage rating can cause the premature failure of the capacitor or, in a scenario, a catastrophic failure that could damage the entire system.
Another consideration is the safety factor. Engineers often choose High Voltage Capacitor Units with a higher voltage rating than the voltage expected in the system. This provides a safety margin to account for voltage spikes or transient overvoltages that could occur due to system faults or other unexpected events. This practice helps to ensure the longevity and reliability of the High Voltage Capacitor Unit.
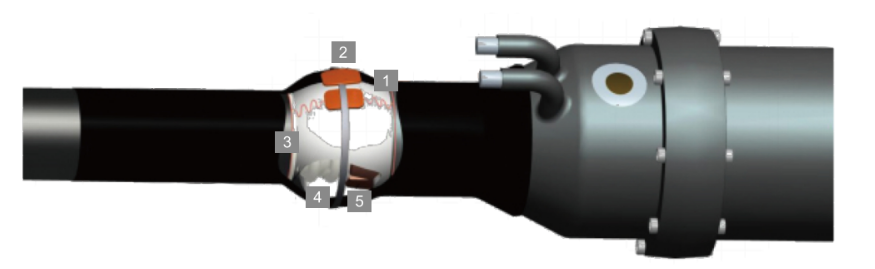
The dielectric material used in High Voltage Capacitor Units also plays a significant role in determining the voltage rating. Materials such as polypropylene, polyester, and oil-impregnated paper are commonly used for their insulating properties. Each material has its own dielectric strength, which directly influences the voltage the High Voltage Capacitor Unit can handle.
In addition to the dielectric material, the physical construction of the High Voltage Capacitor Unit also affects its voltage rating. Factors such as the thickness of the dielectric, the design of the electrodes, and the presence of any internal barriers or shields can all impact the High Voltage Capacitor Unit's ability to withstand high voltages.
In summary, the voltage ratings of High Voltage Capacitor Units are a complex subject that encompasses the material properties of the dielectric, the design of the capacitor, and the specific requirements of the application. Understanding these ratings is crucial for engineers and technicians who are responsible for specifying, installing, and maintaining High Voltage Capacitor Units in power systems. By selecting the appropriate voltage rating, they can ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of the electrical systems in which these High Voltage Capacitor Units are used.
Recommended Products
The variety of models, to meet the development needs of various regions in the world.
-
Add: No. 508, Dongye Road, Dongjing Town, Songjiang District, Shanghai
-
Tel: +86-13757652508
-
E-mail: [email protected]
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى